Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH)
A “Zero Home” refers to a home that produces as much energy as it consumes annually through a combination of energy efficiency measures and on-site renewable energy sources.
Zero Energy Ready Home
A “Zero Home” refers to a building that produces as much energy as it consumes annually through a combination of energy efficiency measures and on-site renewable energy sources. These homes are designed to be highly energy-efficient, minimizing their energy footprint and reducing their carbon emissions.
High Energy Efficiency:
Zero homes are built with advanced insulation, high-performance windows and lighting, and efficient heating and cooling systems.
On-Site Renewable Energy:
They generate electricity using renewable energy sources like solar panels, which are designed to offset the home’s annual energy consumption.
Reduced Carbon Emissions:
By minimizing energy consumption and generating renewable energy, zero homes significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Savings:
While the initial cost of building a zero home may be higher, they can save money on energy bills in the long run.
Examples of Zero Home Concepts:
Net Zero Home:
A home that produces enough renewable energy to offset all its energy consumption, resulting in a net zero energy balance.
Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH):
A high-performance home designed to be so energy-efficient that a renewable energy system can offset most or all of its annual energy use, according to the Department of Energy (DOE).
Passive House:
A very energy-efficient building standard that emphasizes air tightness, high insulation, and efficient heating and cooling systems.
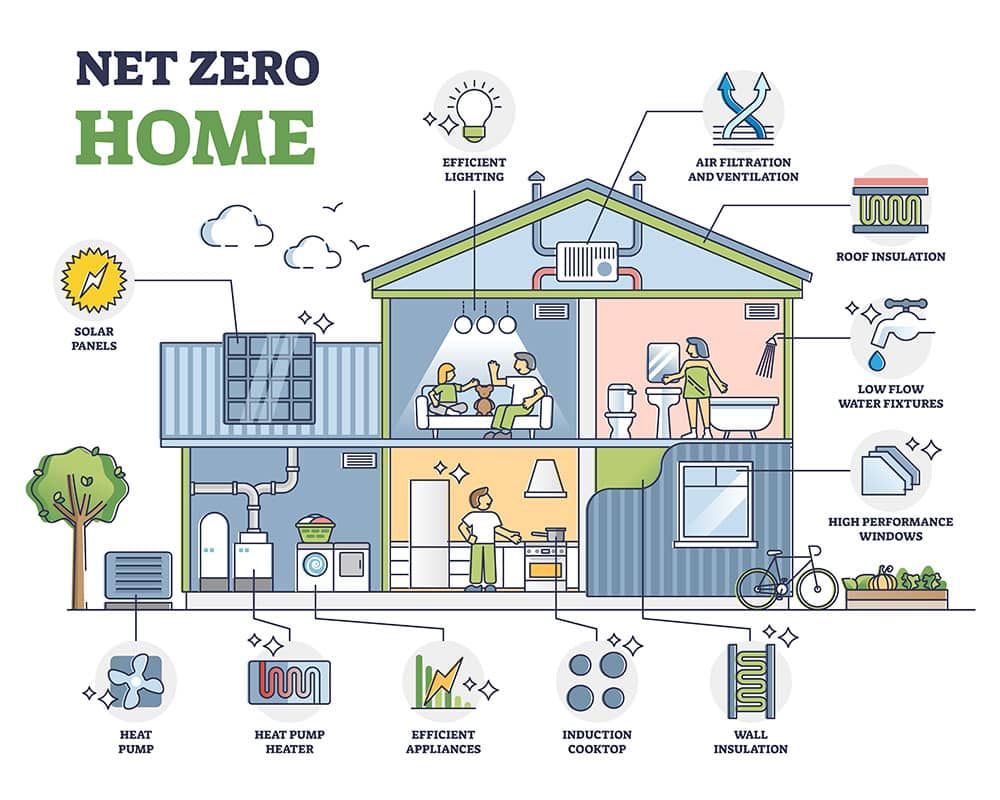
Benefits of Zero Homes:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Lower energy bills due to high energy efficiency and on-site renewable energy.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller ecological footprint.
- Improved Comfort and Health: High-performance homes often offer better indoor air quality and more comfortable living conditions.
- Increased Durability: Well-designed and constructed zero homes are built to last.
Special type of wall insulation ICF
In construction, ICF stands for Insulated Concrete Forms, which are hollow, rigid foam blocks used to create walls and foundations, providing both structure and insulation in one step, often resulting in energy-efficient and durable buildings.
Special Insulated Windows
Argon gas-filled windows are windows with the space between two or more panes of glass filled with argon gas. Argon gas is a dense, colorless, and odorless gas that is used to improve the insulation of windows. By filling the space between the panes, argon gas reduces heat transfer, making the windows more energy-efficient.
